Introduction to Off-Road Trucks Off-road trucks represent a special category of vehicles...
How Soyuz Powers Missions to the International Space Station
The Soyuz spacecraft, a cornerstone of human spaceflight since 1967, is a Russian-designed vehicle that ferries astronauts and cosmonauts to the International Space Station (ISS) and back. Launched atop a Soyuz rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, it comprises three modules: the orbital module, descent module, and service module.
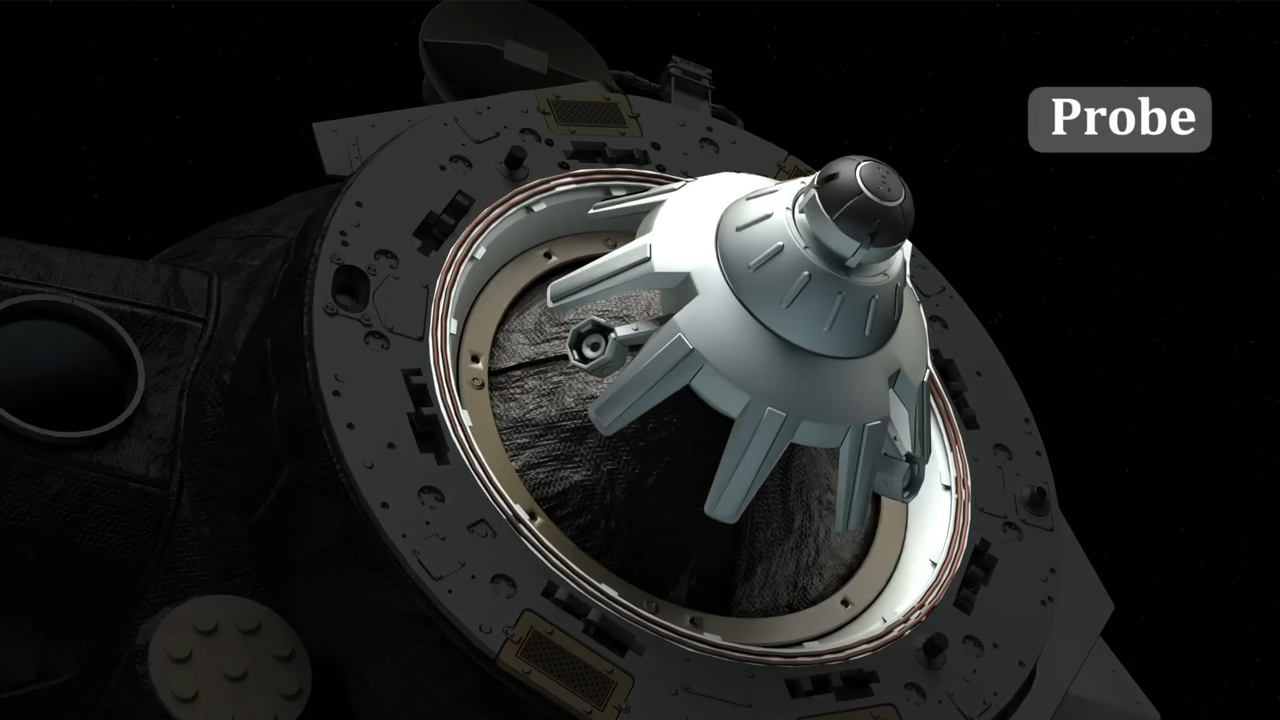
The orbital module, a spherical section at the spacecraft’s front, houses equipment for docking with the ISS and provides living space during orbit, but it is discarded before reentry. The descent module, located in the middle, is where the crew of up to three resides during launch and reentry. It features a heat shield, parachutes, and braking engines to ensure a safe, albeit bumpy, landing in Kazakhstan’s steppes. The service module, at the rear, contains propulsion, life support, and power systems, including solar panels and batteries, and is also jettisoned before reentry.
The Soyuz, weighing 7 tons and measuring 7.2 meters long, reaches orbit in just nine minutes after launch, with the rocket separating post-launch. The journey to the ISS can take six hours or two days, depending on the mission profile, while return trips last about 3.5 hours.
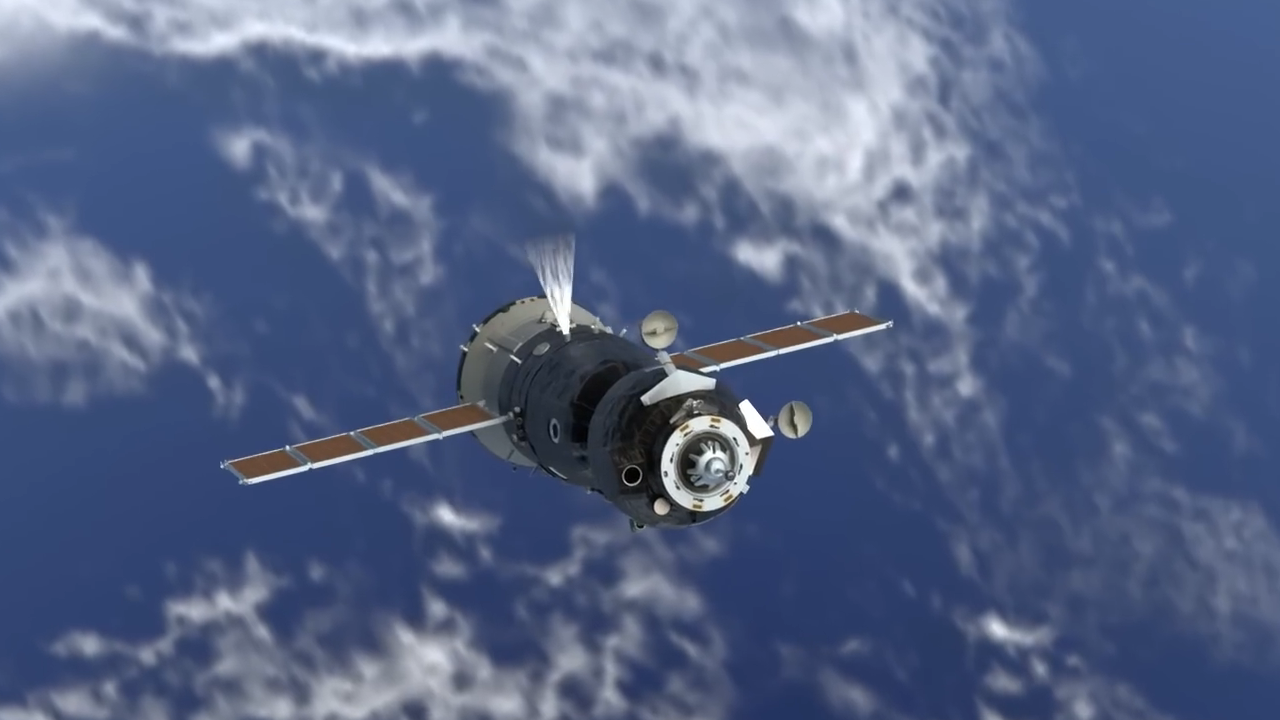

The spacecraft’s design, rooted in the Soviet lunar program, has evolved through versions like the Soyuz-T, TMA, and current MS, incorporating upgrades such as LED lighting, larger solar panels, and improved docking systems. The Soyuz MS, operational since 2016, features a “headlight” shape with a hemispherical upper section, a conical midsection, and a curved heat shield, allowing slight lift during reentry for better control.
The descent module’s 4 cubic meters of internal volume is cramped, with only 2.5 cubic meters usable for the crew. Safety enhancements, including mandatory pressure suits during launch and landing, were introduced after tragedies like Soyuz 1 (1967), where a parachute failure killed cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov, and Soyuz 11 (1971), where depressurization killed the crew.

Soyuz employs a Hohmann transfer orbit for efficient deorbiting, firing its main engine on the Earth’s “dawn” side to slow down and reenter. Atmospheric drag and parachutes decelerate the descent module, with small rocket engines firing just before touchdown to reduce impact to under 2 m/s. The spacecraft’s reliability, with over 140 flights and a 98% success rate, stems from its simple, robust design, including a unique ignition system using wooden sticks in the rocket’s combustion chamber. It served as the sole crew transport to the ISS from 2011 to 2020, post-Space Shuttle retirement, and remains critical for ISS operations, often as an emergency escape craft.
The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975 highlighted its docking capabilities, using a specialized docking module to connect with an Apollo spacecraft, marking the first U.S.-Soviet space collaboration. Today, Soyuz supports international crews, including NASA astronauts, under a seat-swap program with Roscosmos, ensuring redundancy for ISS operations despite geopolitical tensions.
Its thermal protection, life support, and communication systems, like the Rassvet radio and Klyost-M television, ensure crew safety and mission success. While private spacecraft like SpaceX’s Crew Dragon have emerged, Soyuz’s cost-effectiveness and proven track record make it a mainstay of human spaceflight.
Share:
Don't miss those
Sumo-Size Feast: Exploring the Massive Katsudon...
Japanese cuisine has long been celebrated for its balance of flavors, textures,...
Newly Upgraded B-1B Lancer Just Shocked...
The US Air Force has once again made headlines with the newly...
Real-Life Superhuman Moments Captured on Camera
In a world where challenges often seem overwhelming, glimpses of real-life heroes...
3 months ago
Billion Tons of Sugarcane: The Art...
Sugarcane, a towering tropical grass, is the backbone of global sugar production,...
3 months ago
U.S. Navy Pioneers Aerial Refueling Drone...
On August 23, 2025, the United States Navy marked a historic milestone...
3 months ago








